About
A data logger (or datalogger) is an electronic instrument that records data over time or in relation to location. Increasingly, but not necessarily, they are based on a digital processor (or computer). They may be small, battery powered and portable and vary between general purpose types for a range of measurement applications to very specific devices for measuring in one environment only.It is common for general purpose types to beprogrammable. Standardisation of protocols and data formats is growing in the industry and XML is increasingly being adopted for data exchange. The development of the Semantic Web is likely to accelerate this trend. A smart protocol, SDI-12, exists that allows some instrumentation to be connected to a variety of data loggers. The use of this standard has not gained much acceptance outside the environmental industry.
The Extensible Markup Language
XML is a text-based markup language that is fast becoming the standard for data interchange on the Web. As with HTML, you identify data using tags (identifiers enclosed in angle brackets, like this: <...>). Collectively, the tags are known as "markup". But unlike HTML, XML tags identify the data, rather than specifying how to display it. Where an HTML tag says something like "display this data in bold font" (...), an XML tag acts like a field name in your program. It puts a label on a piece of data that identifies it .
|
Data Logging Versus Data Acquisition
The terms data logging and data acquisition are often used interchangeably. However, in a historical context they are quite different. A data logger is a data acquisition system, but a data acquisition system is not necessarily a data logger.
Data loggers are implicitly stand-alone devices, while typical data acquisition system must remain tethered to a computer to acquire data. This stand-alone aspect of data loggers implies on-board memory that is used to store acquired data. Sometimes this memory is very large to accommodate many days, or even months, of unattended recording. This memory may be battery-backed static random access memory, flash memory or EEPROM.
About The Modbus Protocol
Modbus is a serial communications protocol published by Modicon in 1979 for use with its programmable logic controllers (PLCs). It is has become a de facto standard communications protocol in industry, and is now the most commonly available means of connecting industrial electronic devices.
About The Sdi-12 Protocol
SDI-12 stands for serial data interface at 1200 baud. It is a standard to interface battery powered data recorders with micro-processor based sensors designed for environmental data acquisition (EDA).
Usage Of Micro-Processor Based Sensors
A micro-processor in the sensor may calibrate the sensor, control sensor measurements, and convert raw sensor readings into engineering units. The micro-processor also controls the SDI-12 interface. It accepts and decodes instructions received from the data recorder, starts the measurements, controls all timing, and uses the SDI-12 protocol to communicate with the data recorder.
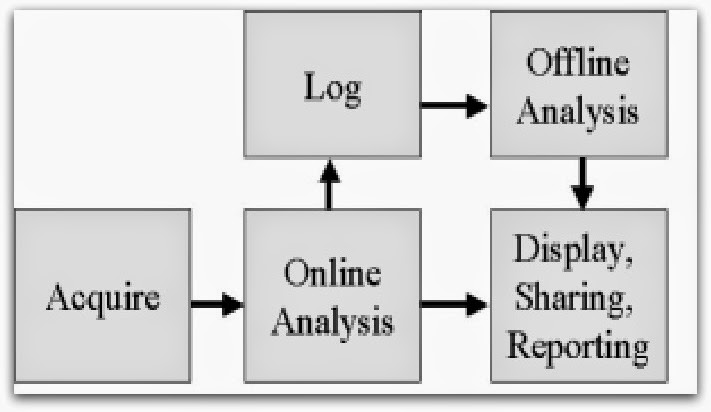
Online Analysis
This step includes any analysis you would like to do before storing the data. A common example of this is converting the voltage measurement to meaningful scientific units, such as degrees Celsius. You can complete these complex calculations and data compression before logging the data. Controlling part of a system based on current measurements -- for example, a kill switch -- is also part of online analysis.
Conclusion
Data Loggers are changing more rapidly now than ever before. The original model of a stand alone data logger is changing to one of a device that collects data but also has access to wireless communications for alarming of events and automatic reporting of data. Dataloggers are beginning to serve web pages for current readings, email their alarms and FTP their daily results into databases or direct to the users. Technically speaking, a data logger is any device that can be used to store data.